Configuration
We currently use the following gems for configuring the application:
dotenv
This gem is used for configuring environment variables for test and development environments. Examples:
REDIS_URLFASTLY_API_KEYSTRIPE_SECRET_KEY
Settings managed via your ENV can be found in Configuring Environment Variables) and viewed at /admin/customization/config (see the Admin guide):
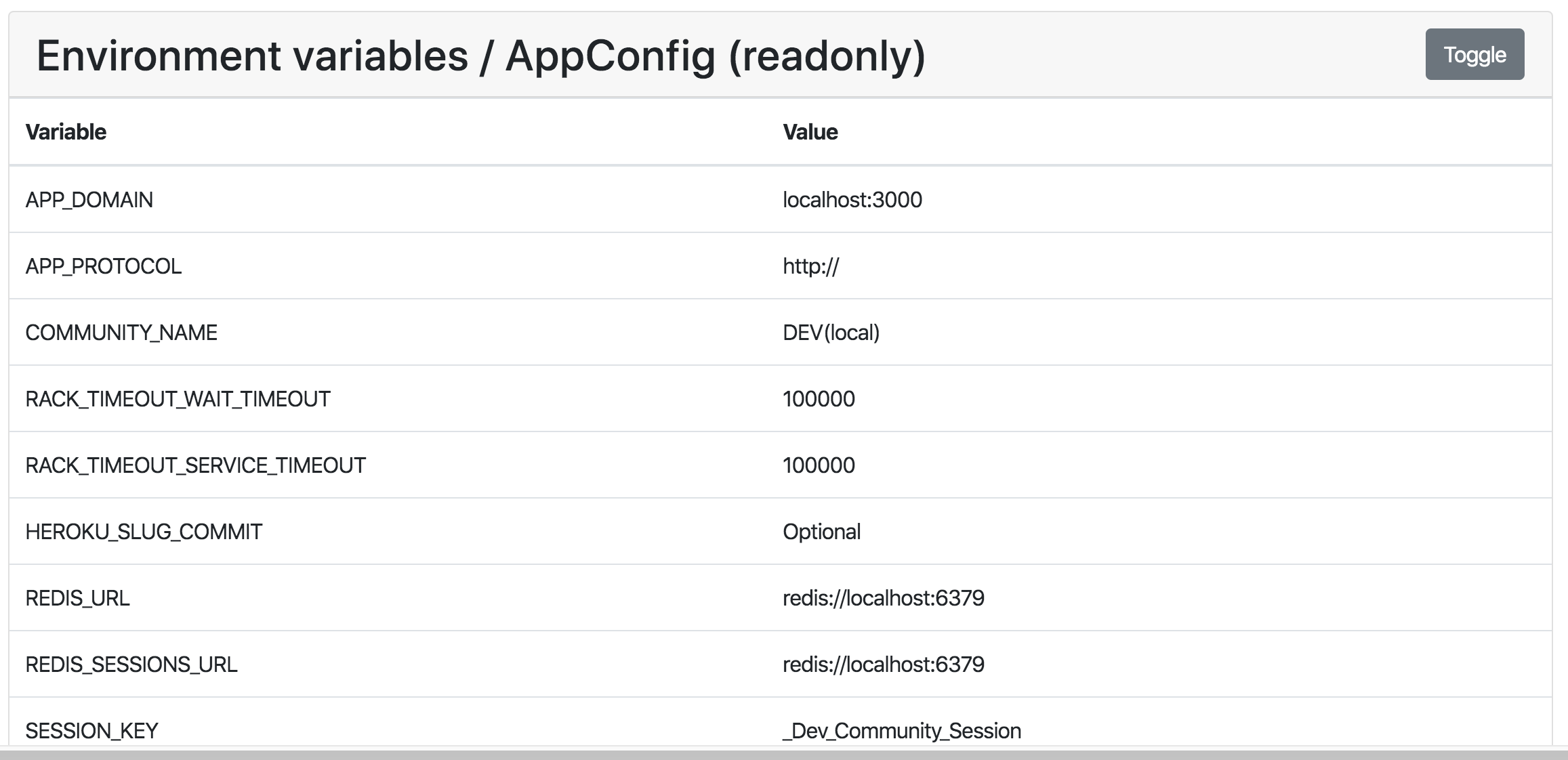
rails-settings-cached
We use this gem for managing settings used within the app's business logic. Examples:
Settings::General.main_social_imageSettings::RateLimit.follow_count_dailySettings::Authentication.twitter_secret
These settings can be accessed via the Settings::General object and various models in the Settings:: namespace and viewed / modified via /admin/customization/config (see the Admin guide).

Vault
The vault Ruby gem allows us to interact with Vault. In a nutshell, Vault is a tool for securely storing and accessing secrets. It is completely optional for running a Forem. To access it we use the wrapper AppSecrets.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19class AppSecrets def self.[](key) result = Vault.kv(namespace).read(key)&.data&.fetch(:value) if ENV["VAULT_TOKEN"].present? result ||= ApplicationConfig[key] result rescue Vault::VaultError ApplicationConfig[key] end def self.[]=(key, value) Vault.kv(namespace).write(key, value: value) end def self.namespace ENV["VAULT_SECRET_NAMESPACE"] end private_class_method :namespace end
We attempt to access a secret from Vault if it is enabled, i.e. if the VAULT_TOKEN is present. If Vault is not enabled or if we cannot find the secret in it, then we fallback to fetching the secret from the ApplicationConfig.
One advantage of using Vault with Forem is that it allows you to update your secrets easily through the application rather than having to mess with ENV files. If you would like to try out Vault, follow our installation guide for setting it up locally.